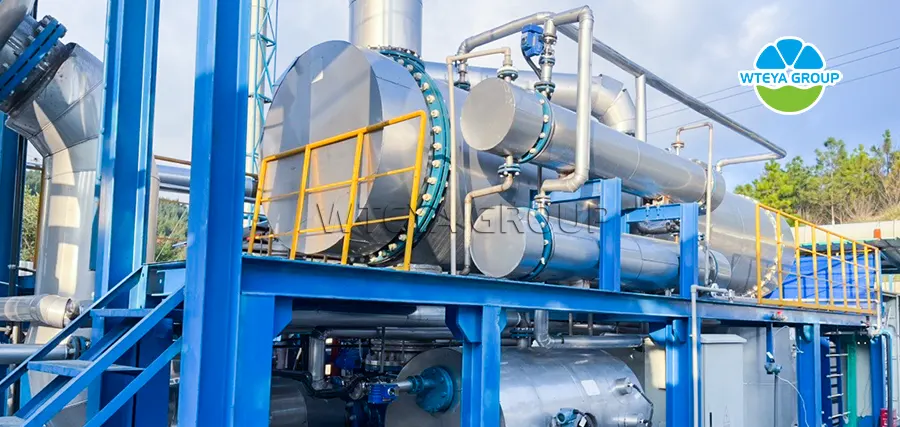


1. Evaporation equipment: such as MVR evaporation equipment, forced circulation equipment, low temperature evaporation equipment, multi-effect evaporation equipment
Which production link is it used in
- Wastewater Treatment and Zero Discharge (ZLD)
High salt wastewater treatment: The wastewater produced in the petrochemical production process usually contains high concentrations of inorganic salts, organic matter and heavy metals and other pollutants. Evaporation equipment (such as multi-effect evaporator, MVR evaporator, thermal steam recompression evaporator, etc.) can separate the water in the wastewater by evaporation, concentrate the wastewater to a near saturation state, and then further treatment by crystallization, drying and other means to achieve the reduction of wastewater or even zero discharge, reducing the impact on the environment.
Emulsion and oil-water mixture treatment: For the wastewater containing emulsified oil and oil-water mixture, most of the oil phase is separated by pre-treatment means such as emulsion breaking and air flotation, and the remaining oily wastewater is further separated by evaporation equipment, so as to recover oil products, reduce oil content in wastewater, and achieve environmental protection discharge standards.
- Process optimization
Solvent recovery: In the petrochemical production process, solvents are often used for extraction, washing, dehydration and other operations. The evaporation equipment can efficiently recover and recycle these solvents, such as toluene, xylene, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, etc., reducing production costs, reducing solvent losses, and reducing organic exhaust emissions.
Product refining and concentration: For some intermediate products or final products, such as alcohols, ketones, acids, etc., evaporation equipment can be used to further purify or concentrate, improve product quality, and meet the requirements of downstream processes or customers for product purity and concentration.
- Resource recovery and by-product treatment
Salt crystallization and recovery: In some chemical processes or wastewater treatment, evaporation equipment can concentrate salt-containing wastewater to saturation, and separate valuable salts, such as sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, and calcium chloride, through cooling crystallization to achieve resource recovery.
Heavy metal salt concentration and recovery: For the wastewater containing heavy metal ions, the evaporation equipment can concentrate it, which is convenient to recover heavy metal resources by chemical precipitation, electrodeposition and other means, reduce the risk of environmental pollution and increase economic benefits.
- Energy conservation and emission reduction
Waste heat utilization: The waste heat, low-temperature steam or condensate generated in the petrochemical production process can be used as a heat source for evaporation equipment to achieve effective use of energy and reduce overall energy consumption.
Reduce solid waste generation: Wastewater treatment through evaporation equipment can greatly reduce the generation of solid waste (such as evaporation residue), reduce the cost of solid waste disposal, and reduce the pressure on the environment.
- Production of special chemicals
Evaporation crystallization preparation of special salt: In the production of some special chemicals, such as the preparation of high purity anhydrous salt, special crystalline salt, etc., evaporation equipment is one of the key equipment, through the precise control of evaporation and crystallization conditions, to produce products that meet the specific purity and crystal requirements.
- Environmental restoration and management left over from the past
Waste liquid treatment: For the high-salt, high-organic and heavy metal waste liquid left over during the decommissioning or renovation of petrochemical facilities, evaporation equipment can be used as one of the treatment technologies to achieve the safe disposal of waste liquid or resource recovery through evaporation and concentration of waste liquid, and help the environmental restoration of the petrochemical industry.
Technical principle
MVR evaporation equipment: The MVR evaporator is to reuse the energy of the secondary steam generated by itself, thereby reducing the need for external energy. The working process of MVR is to compress the steam at low temperature by the compressor, increase the temperature and pressure, increase the enthalpy, and then enter the heat exchanger to condense, so as to make full use of the latent heat of the steam. In addition to starting the car, the secondary steam that does not need to generate steam from the evaporator during the entire evaporation is compressed by the compressor, the pressure and temperature rise, the enthalpy increase, and then sent to the heating chamber of the evaporator as heating steam to maintain the boiling state.
Forced circulation evaporation equipment: The circulation of the solution in the equipment mainly relies on the forced flow generated by the external power. The cycle speed can generally reach 1.5-3.5 m/s. Large heat transfer efficiency and production capacity. The raw material liquid is driven from bottom to bottom by the circulating pump and flows upward along the tube of the heating chamber. Steam and liquid foam mixture into the evaporation chamber separated, the vapor from the upper part of the discharge, fluid blocked fall, through the conical bottom by the circulation pump suction, and then into the heating pipe, continue the cycle. It has high heat transfer coefficient, anti-salting-out, anti-scaling, strong adaptability and easy cleaning. Suitable for scale, crystallization, heat sensitivity (low temperature), high concentration, high viscosity and containing insoluble solids, such as chemical, food, pharmaceutical, environmental protection engineering, waste liquid evaporation recovery and other industries.
Low-temperature evaporation equipment: Low-temperature evaporation refers to the evaporation process with an operating temperature generally between 35 and 50 ° C. After the original bucket reaches the medium level, the pump runs to produce vacuum, the evaporator automatically enters water, and the compressor runs to generate heat to heat the wastewater in the evaporation tank. In the vacuum state, the wastewater temperature rises to about 30℃, and the wastewater begins to evaporate, and the preheating is completed. The evaporation temperature is set at 35-40℃, the compressor compresses the refrigerant to generate heat, and the water evaporates rapidly. At the same time, the refrigerant absorbs heat and refrigeration after gasification through the expansion valve, and the vapor rises and liquefied into the cold liquid into the water storage tank. The refrigerant absorbs heat, and then compresses and heats the waste water. If bubbles rise during the evaporation process, the sensor detects that the defoamer is automatically added to the defoamer, and after a cycle is completed, the concentrated liquid is discharged (the time of a cycle can be set). After one evaporation cycle is completed, the compression pump stops working, the concentrate pipeline pneumatic valve is opened, the evaporation tank is pressurized, and the concentration hydraulic pressure is put into the concentration tank.
What can we achieve
Our evaporation equipment under different water quality conditions, can reach 5-100 times concentration ratio, evaporator with its high efficiency and energy saving, strong adaptability, high degree of automation, environmental safety and stable operation advantages, in the food industry, pharmaceutical industry, chemical industry, environmental protection field and energy field and other industries have been widely used.
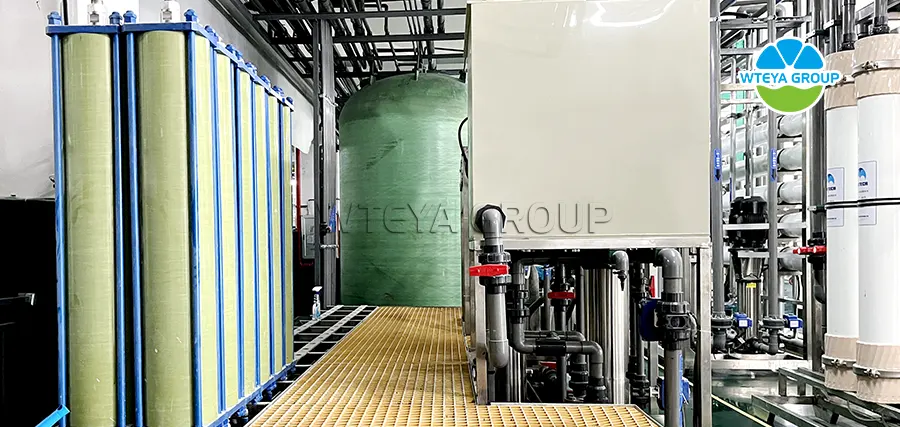

Membrane separation equipment: DTRO, STRO, NF, etc
Which production link is it used in
Membrane separation technology has a wide range of applications in the petrochemical industry, mainly in the following aspects:
(1) Treatment of crude oil and refined oil
Desalination and dehydration: In the process of crude oil extraction and transportation, crude oil usually contains a certain amount of salt and water. Membrane separation technology (such as reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, etc.) can efficiently remove salt and water in crude oil, protect refining equipment from corrosion, and improve refining efficiency and product quality.
Oil refining: Through membrane separation technology, the refined oil (such as gasoline, diesel, lubricating oil, etc.) can be deeply purified to remove impurities such as sulfide, nitride, aromatics, olefins, etc., improve the combustion performance of oil products, reduce exhaust emissions, and meet the increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
(2) Gas separation and purification
Hydrogen recovery and purification: In refinery hydrocracking, reforming and other processes, a large amount of hydrogen rich exhaust gas is produced. Membrane separation technologies (such as gas separation membranes, pervaporization membranes, etc.) efficiently separate and recover hydrogen while removing impurity gases (such as CO, CO₂, CH₄, etc.) in it, providing high purity hydrogen for subsequent hydrogen recycling or fuel cell applications.
Natural gas dehydration and desulfurization: In natural gas processing, membrane separation technology is used to remove water in natural gas (such as dehydration using polymer membranes) and sulfide (such as desulfurization using sulfide separation membranes), to ensure the quality of natural gas and transportation safety.
(3) Catalyst recovery and recycling
Catalyst mother liquor treatment: In the process of catalytic cracking, hydrotreating, etc., the catalyst will form a mother liquor with the reactants. The membrane separation technology can effectively separate the catalyst from the liquid product, realize the recovery and recycling of the catalyst, reduce the catalyst cost and reduce the waste generation.
(4) Recovery and recycling of organic solvents
Solvent dehydration and purification: In the petrochemical production process, many processes use organic solvents (such as toluene, xylene, ethanol, etc.). Membrane separation technology enables efficient recovery and recycling of these solvents, reducing production costs and solvent losses, while also reducing organic exhaust emissions.
(5) Wastewater treatment and resource recovery
High salt wastewater treatment: petrochemical wastewater usually contains high concentrations of inorganic salts, organic matter and heavy metals and other pollutants. Membrane separation technology (such as reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, electric drive membrane, etc.) can trap most of the salt and harmful substances in the wastewater, so that the wastewater can be deeply treated, and the wastewater can be reduced, recycled and discharged to the standard. Recovery of useful components: membrane separation technology can be used to recover valuable components in wastewater, such as amino acids, organic acids, alcohols, ketones, etc., to separate them out and return to the production process to achieve resource recycling and reduce production costs.
Technical principle
The process of selective separation of components in a liquid or gas mixture using special films. The main principle of this technique is based on the differences in the speed and ability of different components to penetrate the membrane, which may be determined by the properties of the components, the characteristics of the membrane, and the concentration difference on both sides of the membrane, the pressure gradient, the potential gradient or the partial pressure of the vapor. Membrane separation methods include microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis, each of which is suitable for different separation needs. For example, microfiltration and ultrafiltration screen molecules or solutes of different sizes based on the micropore size of the membrane; Reverse osmosis is to make the solvent pass through the membrane and the solute be trapped at a pressure higher than the osmotic pressure of the solution. Electrodialysis is the selective separation of ions in solution by ion exchange membrane under the action of electric field.
What can we achieve
Membrane separation technology is applied in the petrochemical industry in the treatment of crude oil and refined oil, gas separation and purification, catalyst recovery and recycling, organic solvent recovery and recycling, wastewater treatment and resource recovery, environmental monitoring and management and other links, which is of great significance to improve resource utilization, reduce production costs, reduce environmental pollution, and achieve green and sustainable development.
ECC Catalytic oxidation equipment:
Which production link is it used in
ECC catalytic oxidation equipment should be mainly used for the removal of organic matter in high salt liquid in petrochemical industry. It can also kill the microorganisms in the water to ensure the pure water of the feed liquid, providing a guarantee for the normal operation of the equipment.
Technical principle
ECC catalytic oxidation technology is a new technology developed by our company, which uses catalysts to promote the oxidation reaction between organic pollutants and oxidants (such as oxygen, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, etc.) under specific conditions to generate harmless or low-toxic end products and achieve effective removal of pollutants. Different catalytic oxidation equipment adopts different oxidants, catalysts and reaction conditions according to different applications and treatment objects to meet various actual needs.
What can we achieve
The removal efficiency of such products on organic matter (CODcr) can reach less than 80%, and some can be more than 95%. It can also greatly reduce the probability of foam occurrence in high temperature reactor, evaporation equipment and scale formation in membrane system.
Get a free quote!
Let professionals help you choose
Our Customers And Services










