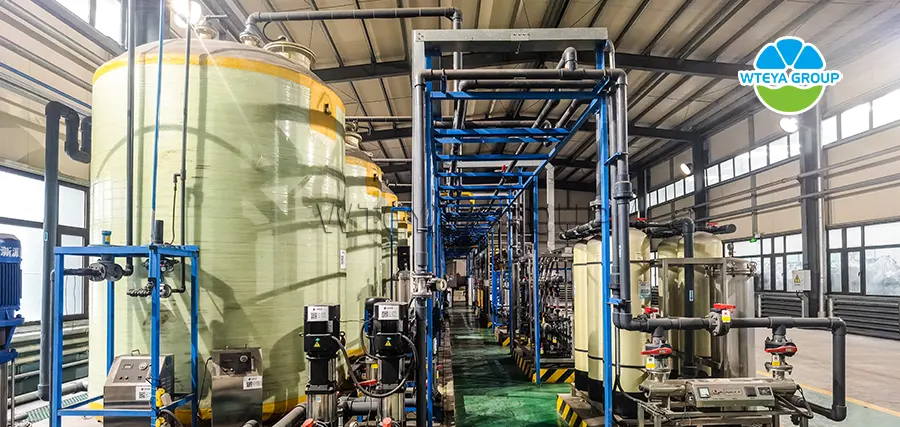


1. Integrated pretreatment equipment
Applied in which production process
This type of equipment is mainly used for ore mining, ore pretreatment, including flotation, crushing, and grinding.
Technical Principles
This type of equipment mainly uses natural sedimentation and coagulation sedimentation technology, filtration and centrifugal separation technology, etc. to perform solid-liquid separation and remove impurities from the feed liquid.
What effects can we achieve
We can achieve fully automated operation and unmanned operation of such devices, saving a lot of manpower; The removal efficiency of suspended solids (SS) can reach 80-95% of the treatment effect.
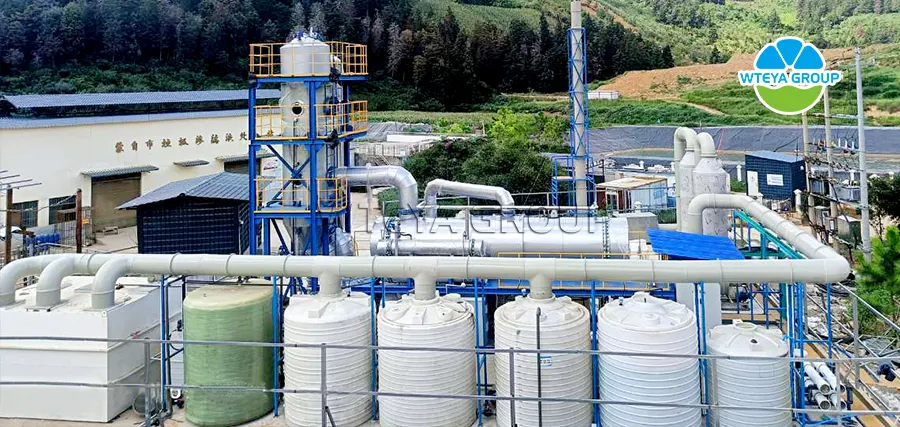

2. Evaporation equipment: such as MVR evaporation equipment, forced circulation equipment, low-temperature evaporation equipment, and multi effect evaporation equipment
Applied in which production process
Our company's equipment mainly uses metal concentration, purification, and recovery of sulfates and carbonates; It can also be used in processes such as high salt wastewater treatment and reclaimed water reuse.
The application of evaporation equipment in the battery positive electrode material industry is mainly concentrated in wet metallurgical processes, especially in raw material purification, solution concentration, by-product treatment, and wastewater treatment, as follows:
- Raw material purification and solution concentration
Lithium salt solution concentration: In the production of battery positive electrode materials, such as preparing lithium iron phosphate (LFP), it is necessary to react phosphoric acid with lithium salts (such as lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide). Evaporation equipment can be used to concentrate lithium salt solutions, increase their concentration, facilitate better reaction with phosphoric acid, and reduce energy consumption in subsequent drying processes.
Precursor solution evaporation crystallization: In the preparation process of certain positive electrode materials, such as co precipitation method to prepare nickel cobalt lithium manganese oxide (NCM) precursors, it is necessary to convert the metal salts in the reaction solution into solid precursor powder through evaporation crystallization. The evaporation equipment plays a crucial role in this process, ensuring that the morphology, particle size distribution, and purity of precursor particles meet the requirements of subsequent sintering processes by controlling the evaporation rate and crystallization conditions.
- Byproduct treatment and resource recovery
Mother liquor recovery and regeneration: In the process of hydrometallurgy, after steps such as precipitation and extraction, mother liquor containing unreacted metal ions or by-products will be produced. Evaporation equipment can be used to concentrate these mother liquids, recover valuable metal ions, and reduce waste generation, achieving resource recycling.
Wastewater treatment: During the production process of positive electrode materials, salt containing wastewater may be generated. Evaporation equipment can evaporate the moisture in wastewater to form crystalline salts and distilled water. Crystalline salts can be further treated or utilized as resources, while distilled water can be reused in the production process or discharged to meet standards, achieving the reduction and resource utilization of wastewater.
- Wastewater treatment and zero discharge (ZLD)
High salt wastewater treatment: The wastewater generated during the production process of battery positive electrode materials may contain high concentrations of inorganic salts and heavy metal ions. Evaporation equipment (such as multi effect evaporators, MVR evaporators, etc.) can evaporate the moisture in wastewater to form concentrated liquid and distilled water. Concentrated liquid can be further solidified for treatment or resource utilization, while distilled water can be reused in the production process or discharged to meet standards, achieving the reduction and resource utilization of wastewater.
- Energy conservation and emission reduction
Waste heat utilization: The waste heat, low-temperature steam, or condensate generated during the production process of battery positive electrode materials can serve as a heat source for evaporation equipment, achieving effective energy utilization and reducing overall energy consumption.
Reducing solid waste generation: Treating wastewater through evaporation equipment can greatly reduce the generation of solid waste (such as evaporation residue), lower the cost of solid waste disposal, and alleviate environmental pressure.
- Historical legacy of environmental restoration and governance
Waste liquid treatment: For high salt and heavy metal waste liquid left by battery positive electrode material production enterprises, evaporation equipment can be used as one of the treatment technologies. Through evaporation and concentration of waste liquid, safe disposal or resource recovery of waste liquid can be achieved, helping enterprises to restore the environment.
Technical Principles
- MVR evaporator equipment: The MVR evaporator reuses the energy of the secondary steam it generates, thereby reducing the demand for external energy. The working process of MVR is to compress the low-temperature steam through a compressor, increase the temperature and pressure, increase the enthalpy, and then enter the heat exchanger for condensation to fully utilize the latent heat of the steam. Except for start-up, the entire evaporation process does not require the generation of steam. The secondary steam coming out of the evaporator is compressed by the compressor, which increases pressure and temperature, enthalpy, and then sent to the heating chamber of the evaporator for use as heating steam, maintaining the boiling state of the material liquid.
- Forced circulation evaporation equipment: The circulation of solution inside the equipment mainly relies on the forced flow generated by external force. The cycle speed can generally reach 1.5-3.5 meters per second. High heat transfer efficiency and production capacity. The raw material liquid is pumped from bottom to top by a circulating pump and flows inward and upward along the heating chamber tube. After entering the evaporation chamber, the mixture of steam and liquid foam separates, and the steam is discharged from the upper part. The fluid is blocked and falls down. It is sucked in by the circulation pump at the conical bottom and then enters the heating tube to continue circulation. It has a high heat transfer coefficient, resistance to salt precipitation, anti scaling, strong adaptability, and is easy to clean. Suitable for evaporative concentration in chemical, food, pharmaceutical, environmental engineering, waste liquid evaporation and recovery industries with scaling, crystallinity, thermal sensitivity (low temperature), high concentration, high viscosity, and insoluble solids.
- Low temperature evaporation equipment: Low temperature evaporation refers to an evaporation process that operates at temperatures generally between 35-50 ℃. After the raw water bucket reaches the middle liquid level, the water pump operates to generate a vacuum, and the evaporator automatically receives water. The compressor operates to generate heat to heat the wastewater in the evaporation tank. Under vacuum, the wastewater temperature rises to around 30 ℃, and the wastewater begins to evaporate. Preheating is completed. The evaporation temperature is set to 35-40 ℃, and the compressor compresses the refrigerant to generate heat. While the water evaporates rapidly, the refrigerant absorbs heat and cools through the expansion valve after gasification. The vapor rises and liquefies with the cold liquid, entering the water storage tank. The refrigerant absorbs heat and compresses it through the compressor to heat up the wastewater. If there are bubbles rising during the evaporation process, the sensor will detect it and automatically add defoamer. After one cycle is completed, the concentrated solution will be discharged (the time of one cycle can be set). After one evaporation cycle is completed, the compression pump stops working, the pneumatic valve of the concentration liquid pipeline opens, the evaporation tank is pressurized, and the concentration hydraulic pressure is fed into the concentration tank.
What effects can we achieve
Our company's evaporation equipment can achieve a concentration ratio of 5-100 times under different water quality conditions. Evaporators have been widely used in various industries such as food industry, pharmaceutical industry, chemical industry, environmental protection, and energy due to their high efficiency, energy efficiency, strong adaptability, high degree of automation, environmental safety, and stable operation.
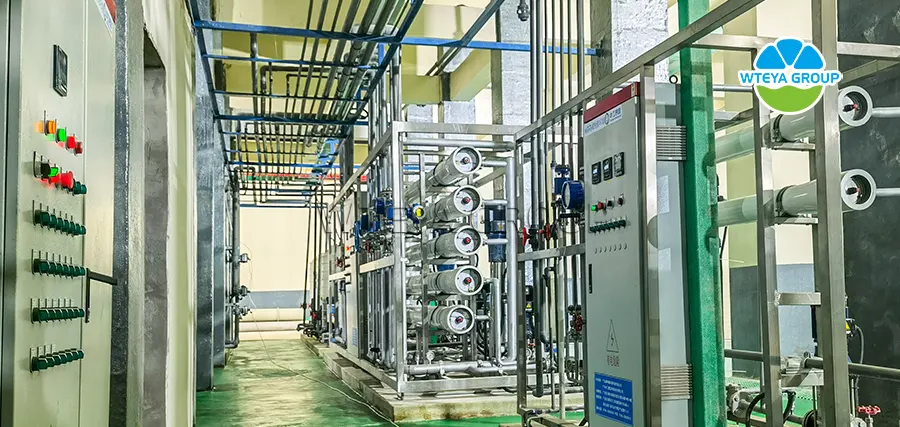

3. Membrane separation equipment: DTRO, STRO, NF, etc
Applied in which production process
Membrane separation equipment has important application value in the production and processing industry of battery positive electrode materials, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- Raw material purification and purification
Ion separation and concentration: Membrane separation technology, especially nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, can be used for deep purification of lithium salt solutions required for the production of positive electrode materials (such as lithium carbonate, lithium sulfate, etc.), effectively removing harmful ions, trace metal impurities, and organic pollutants, improving the purity of lithium salt solutions, and providing high-purity raw materials for the subsequent synthesis of high-quality positive electrode materials.
- Solvent recovery and recycling
In the preparation process of certain positive electrode materials, such as solvothermal method, organic solvents are used. Membrane separation equipment can separate and recover wastewater or waste liquid containing organic solvents, reduce solvent consumption, reduce waste generation, and reduce environmental pollution risks.
- Separation of intermediates and by-products
Precursor washing and grading: In the synthesis stage of precursor materials for positive electrodes, such as co precipitated hydroxides or carbonates, they can be washed and graded through microfiltration (MF) or ultrafiltration (UF) membranes to remove small particle impurities, improve the uniformity and purity of precursor particle size distribution.
Desalination of by-products: In some wet processes, by-product solutions containing high concentrations of inorganic salts are produced. Membrane separation technology can help remove these salts, allowing by-products to be further utilized as resources or safely disposed of.
- Wastewater treatment and recovery
Wastewater reuse: The wastewater generated during the production process of battery positive electrode materials often contains high concentrations of metal ions and other harmful substances. Membrane separation equipment, such as reverse osmosis or nanofiltration membranes, can be used for deep treatment of these wastewater, achieving water resource reuse, reducing fresh water consumption and wastewater discharge.
Heavy metal recovery: For wastewater containing valuable metal ions (such as cobalt, nickel, manganese, etc.), selective interception and recovery can be achieved through special membrane separation technologies such as ion exchange membranes or chelation membranes, achieving the dual goals of resource recovery and environmental protection.
Technical Principles
The process of selectively separating components in liquid or gas mixtures using special thin films. The main principle of this technology is based on the differences in the speed and ability of different components to penetrate the membrane, which may be determined by the properties of the components, the characteristics of the membrane, and factors such as the concentration difference, pressure gradient, potential gradient, or vapor partial pressure on both sides of the membrane. Membrane separation methods include microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and electrodialysis, each of which is suitable for different separation needs. For example, microfiltration and ultrafiltration screen molecules or solutes of different sizes based on the pore size of the membrane; Reverse osmosis is the process of trapping solutes by allowing solvents to pass through a membrane at pressures higher than the osmotic pressure of the solution; Electrodialysis is the selective separation of ions from a solution using ion exchange membranes under the action of an electric field.
What effects can we achieve
Membrane separation equipment can be integrated into continuous and automated production lines to achieve continuous separation, purification, and recovery of materials, which helps to improve production efficiency, reduce quality fluctuations between batches, reduce energy consumption, and conform to the green and efficient production concept of modern battery manufacturing industry.
The application of membrane separation equipment in the production and processing industry of battery positive electrode materials is extensive and important, mainly reflected in raw material purification, intermediate and by-product separation, wastewater treatment and recovery, gas treatment, and promoting continuous production process optimization. It plays a significant role in improving the quality of positive electrode materials, reducing costs, energy conservation and emission reduction, and achieving sustainable production. With the continuous development and improvement of membrane separation technology, its application prospects in the battery material industry will be even broader.
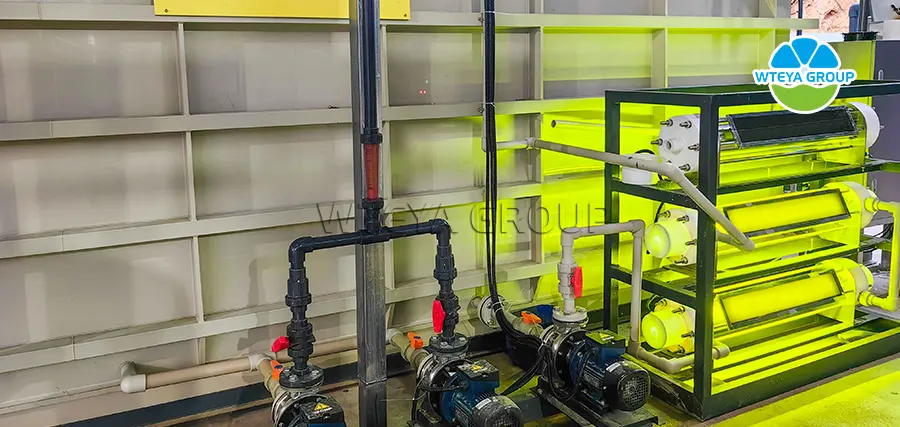
4. ECC catalytic oxidation equipment:
Applied in which production process
ECC catalytic oxidation technology is a new technology developed by our company, which uses catalysts to promote the oxidation reaction between organic pollutants and oxidants (such as oxygen, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, etc.) under specific conditions, generating harmless or low toxic final products, and achieving effective removal of pollutants. Different catalytic oxidation equipment adopts different oxidants, catalysts, and reaction conditions according to different application scenarios and processing objects to meet various practical needs.
Technical Principles
ECC catalytic oxidation technology is a new technology developed by our company, which uses catalysts to promote the oxidation reaction between organic pollutants and oxidants (such as oxygen, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, etc.) under specific conditions, generating harmless or low toxic final products, and achieving effective removal of pollutants. Different catalytic oxidation equipment adopts different oxidants, catalysts, and reaction conditions according to different application scenarios and processing objects to meet various practical needs.
What effects can we achieve
The removal efficiency of such products by the company for organic matter (CODcr) can reach below 80%, and some can exceed 95%. It can also greatly reduce the probability of foam occurrence in high temperature reaction kettle and evaporation equipment and the scaling of membrane system.
Get a free quote!
Let professionals help you choose
Our Customers And Services










